

This is a case study sent to me from National Instruments. I just had to post it as is, because it just shows the serious potential of APIs. If cloud computing and mobile hasn't convinced you that APIs are here to stay, take a look at what National Instruments is doing.
Over the past five years, National Instruments (NI) has been using an API strategy to enable a developer ecosystem, based on their LabVIEW software platform. NI equips engineers and scientists with tools that accelerate productivity, innovation, and discovery – and a strong ecosystem is core to their philosophy. This case study takes a look at one approach, and the business role that APIs play in expanding into new markets.
As background, NI LabVIEW is a productivity tool and graphical programming language used in all kinds of scientific applications. The breadth of users range from “aspiring engineers” who use a specialized version to program the Lego Mindstorms NXT software, to some of the world’s top researchers who use LabVIEW to design complex systems including software for the CERN hadron collider and the SpaceX control center.

Figure 1: LabVIEW is used from K through Rocket Science.
To understand why an API strategy was needed, first consider the standard use-case for LabVIEW. Most companies use LabVIEW as a productivity tool/IDE to develop applications using the default software stack provided by NI, and combining that software with measurement hardware. A common application is production testing of a consumer device, such as the Xbox 360 controller from Microsoft. LabVIEW allows complete customization of an engineering application, just as is possible with any other programming language. The difference between a text-based language, and LabVIEW’s graphical approach, that that the graphical approach is familiar to engineers who grow up drawing block diagrams of systems, and it makes connecting to real-world I/O very efficient. LabVIEW also supports parallelism (multithreading), memory management, built-in analysis, control algorithms, and measurement routines which helps engineering firms build sophisticated applications more quickly.
NI’s core business model is to serve end-users directly, but the ability to scale through an open platform allows “repeatability”. In otherwords, through an API strategy, Company A in one specialized domain, can extend the NI platform or build a vertical product on top of it, such that Company B can leverage that. The software stack for 3rd party developers looks very similar to the stack for end-users, with the addition of APIs that enable product development.
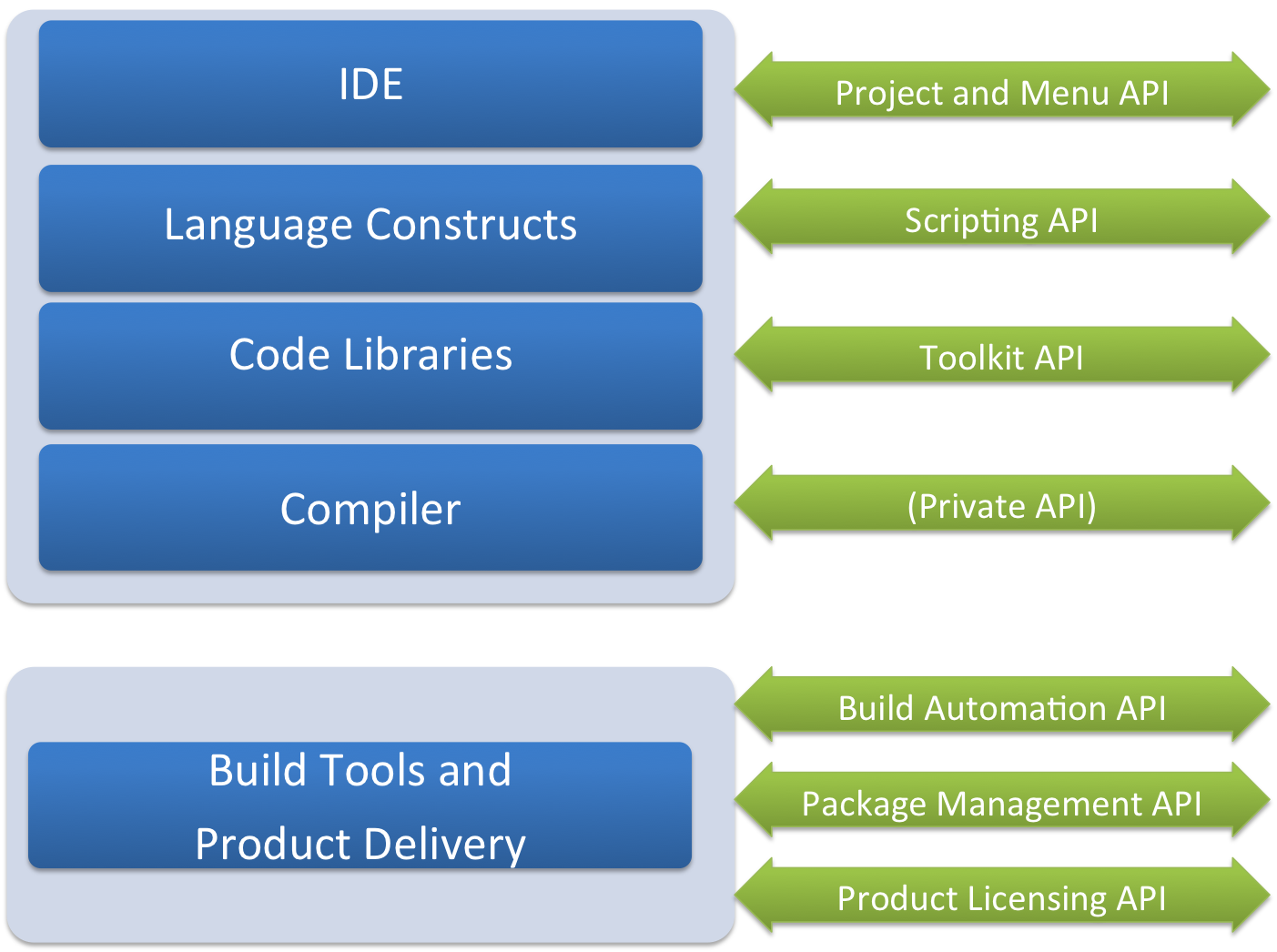
Figure 2: API Framework for LabVIEW
In recent years, there have been some very compelling use-cases that have arisen from the LabVIEW ecosystem, and over 100 certified products in total. Here’s a breakdown of three examples:
- Robotics - ImagingLab GmbH, is a German company that has created LabVIEW toolkits to allow engineers to control industrial robots from leading manufacturers including DENSO, KUKA, Epson, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi, and more.
- Big Data - Neural ID, a venture backed firm in the San Francisco bay area, has created a pattern recognition engine called CURE, to analyze unstructured data. This product sits on top of LabVIEW, and can recognize any kind of waveform and provide analytic capabilities to allow organizations to make better decisions about their data. It’s used by companies like ecoATM and NASA.
- Cloud Computing - Maintainable Software has developed a software-as-a-service product for use in electronics manufacturing test, for cloud-based data management. Their software is used by customers such as Coulomb Technologies, a leader in electric vehicle chargers. In addition, Maintainable Software has deep expertise in tools used to develop cloud infrastructure, and have published a technical book on the subject. Their product works on the latest tablet devices such as Apple iPads.
The companies listed above offer their respective products through NI’s LabVIEW Tools Network, which is an appstore dedicated to engineers and scientists.
In summary, an API strategy can enable 3rd party developers and tech companies to innovate on a mature software platform and expand it into new markets. It’s an approach that’s not just limited to companies in the mobile or web space– it is equally as powerful in the B2B space in industries like test & measurement, and embedded control. For a product like LabVIEW with a 25+ year history, an API strategy is one of the best ways to compliment in-house R&D efforts with an ecosystem approach, and drive innovation in emerging areas like Robotics, Big Data, and Cloud.
