
One of the teams I work closely with at Postman is the group behind mocking APIs with Postman. The ability to statically mock APIs has received a lot of investment when it comes to recent releases, and in a couple of my Postman partner conversations I have been asked for more information about how to mock API using Postman. So, in an effort to reach the widest possible audience as I can, I wanted to write up an overview on the current state of mocking APIs using Postman, to help get everyone up to speed—including myself. ;-)
Overview of Mocks Using Postman
To get started with understanding the value of mocking APIs I recommend visiting the dedicated marketing page Postman has up for mocking APIs. This provides you with the meat of what you’ll need to make the argument for mocks across your team, as well as your leadership.
- See Exactly How Your API will Run—Even Before It's in Production - API design is the key to building quality APIs that last. Postman's mock API servers simplify design and planning, support split-stack development, and help you ensure that your API will run the way it's supposed to in production.
- Shorten Time to Production - Work more efficiently with Postman's API mock servers. Postman mocks support split-stack development so front-end and back-end developers can work in parallel and view responses without spinning up the back end.
- Design Your API with Flexible Schema Support - Postman mock servers complement Postman's extended schema support. Write, edit, or import your API schema to define your API's data structure and generate a collection from your API schema. You can review API responses using mock servers so you can reliably build your API from the ground up—all in one central place.
- Simulate the Expected Behavior of Your API - Postman Mock Servers simulate API responses that applications and services can utilize even before the API is built. Postman matches requests and generate responses to show you how your API will run in production.
- Catch and Fix Bugs Early - Mock servers increase visibility into errors and weak spots in your API, so you can debug effectively and efficiently. You can easily use mock servers to test for response errors continuously or as often as you need throughout the API lifecycle.
- Create Public or Private Mock Servers in Postman - Postman provides two different types of mock servers. Public mock servers are great for open source or individual projects, but if you're working on internal or private APIs, you can easily keep your APIs secure by viewing API responses with private mock servers.
- Visualize Your Data - Postman Visualizer can help turn your API data into charts and graphs. Combined with Postman mocks, developers can utilize Visualizer to help API consumers more easily understand API responses.
This should help you build a case for why you should be mocking. Providing the 100K view of what is possible with Postman mocks, but also understand the business value for your team learning to mock. If you were looking for something a little more substantial don’t worry, the next section will start getting you into the weeds of what it takes to setup mock servers, and make sure you have rich collections available to power your mock APIs.
Setting Up Mock Servers
This section is all about giving you the base you will need to understand how mocks work, and what you will need to setup, work with, and make sense of how Postman mock servers best fit in with your operations. Helping you on-board with the concept of mocking, but then quickly move to something that is functional within your own Postman workspace.
- Creating mock servers - You can create mock servers from an existing collection, or Postman will create a new collection for your mock server.
- Configuring mock details - When you create a mock server you will give it a name, choose a version tag (if your collection has a specific version you want to mock), and select an optional environment to use with the requests.
- Making requests to mocks - With your mock URL, you can start making requests right away. Make sure the request you want to mock has at least one example added to it.
- Using HTTP access control - In addition to using the Postman app to make requests to mock endpoints, you can also make those requests in a browser.
- Viewing mock calls - You can view and search the details of calls to your mock servers using the mock call log.
- Troubleshooting mock calls - You can use the mock call log to troubleshoot your requests to mock servers.
While Postman mock servers are just what is widely considered to be “static mocks”, there is a lot of functionality in there that will help you make these static representations of your APIs much more functional, moving them much closer to what is considered to be “dynamic mocks”—which walks a fine line between dynamic representations of your APIs and actually deploying them.
Mocking with Examples
Mock servers on the Postman platform are all powered by Postman collections, leveraging examples for each individual API request as the potential response for each mocked API. Giving you full control over what gets returned for all of your mocked APIs, allowing you to customize and personalize the static responses that are returned for each API request.
- Setting up some basics - Before you get into the details of mocking, let’s start with setting up some basics required for mocks to work.
- Adding more examples - To further illustrate how responses from the mock service are entirely dependent on your saved examples, let's try adding another example to this collection.
- Using random data dynamic variables - You can use random data dynamic variables in your Mock Server's Example Response Body.
- Using query params - Postman's Mock server functionality is enhanced to return different responses based on matching request query params.
- Mocking GraphQL queries - Postman enables you to mock your GraphQL queries easily.
The robustness and completeness of your examples will define the functionality of your APIs. The more rich your examples are within your Postman collection, the more meaningful your mock APIs will be. For new APIs this will require a significant amount of planning and work to create these examples, but if it is an existing API you can easily make calls to the APIs, save, then edit each response, making quick work of creating what you need to mock your APIs.
Mocking by API
An important dimension of mocking APIs on the Postman platform is the ability to create, manage, and destroy your mock servers using the Postman API. Using the Postman API to automate and orchestrate how you mock your APIs is a great way to reduce the workload when it comes to ensuring there is mock coverage across all of the API you are managing using Postman.
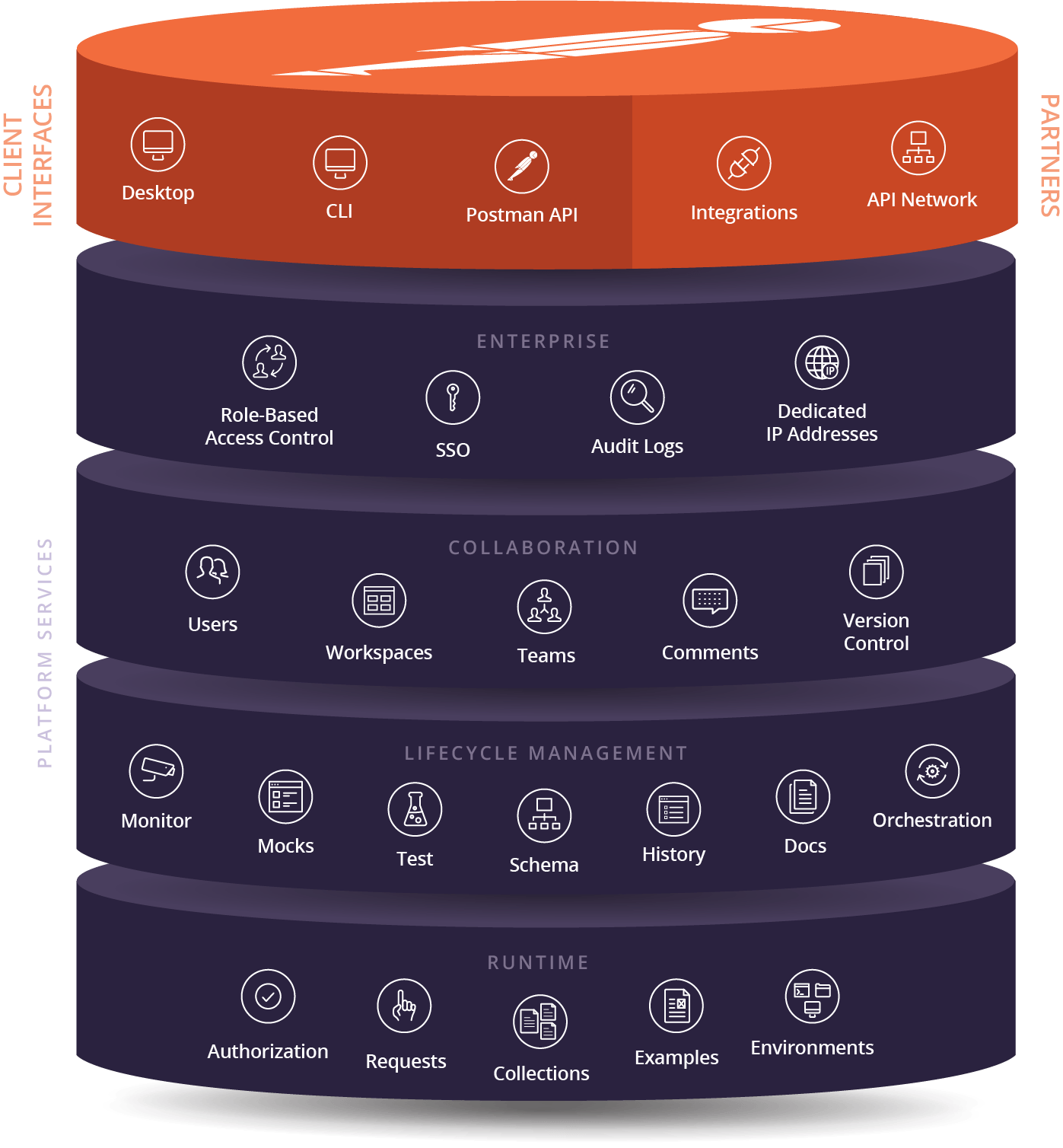
- Set up a collection for mocking - Collectionis are the core of mock servers on Postman, and this will help you understand what is going into each one.
- Retrieve information needed for mock creation - You need a collection and environment to make your mock server work, so this will help make sure you have those, and their unique identifiers.
- Create a mock using the Postman API - With all of the details for your collection and environment you can actually automate the creation of the mock API using the Postman API.
- Run the mock service - This provides you with the details you need to actually begin making calls to the mock server you just setup, providing a common set of patterns for the URL.
The Postman API helps reduce the workload when it comes to crafting the collection you will need, with all of the examples you will need. It also helps you manage the lifecycle and availability of mock servers for different business workflows, going well beyond just having a single reference mock for all of your APIs, and making sure your mocked APIs reference specific business processes that can be executed via your API.
A Few More Resources for Your Journey
That should give you the 100K view of why you should be mocking your APIs, the details you need to make that happen, as well as a look at how you can automate and orchestrate mock APIs using the Postman API. In addition to the marketing and documentation above I recommend taking look at these two videos from our team when it comes to working with mocks via the Postman platform.
- POST/CON 2018 workshop in review: Mock servers - While a little dated, Joyce gives a great walk through of what Postman mock servers can do.
- Building a mock API: Postman live stream on Twitch - Joyce and Arlemi go into some great details about mocking with Postman on a recent live stream.
I am also playing around with a couple of prototypes for mocking APIs using Postman. Going beyond the traditional use cases and pushing Postman mocks into some new areas like publishing simple data APIs using mocks, or providing a specific API business use case via an API sandbox. Like the rest of Postman, there are many different ways you can put mocks to work, so I will be further fleshing out some of the use cases, going beyond just AI design first, testing, and the other common arguments for mock servers. This is the part of my job that I enjoy the most—pushing both the platform and user’s imagination when it comes to what is possible with Postman and the API lifecycle. If there are mock use cases you'd ilke to see as part of Postman mocks, or have specific situations you'd like to explore, feel free to reach out--I am happy to incorporate them into my regular storytelling and evangelism.
